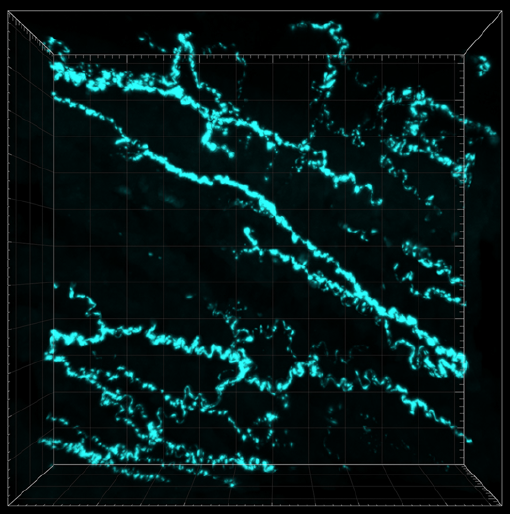
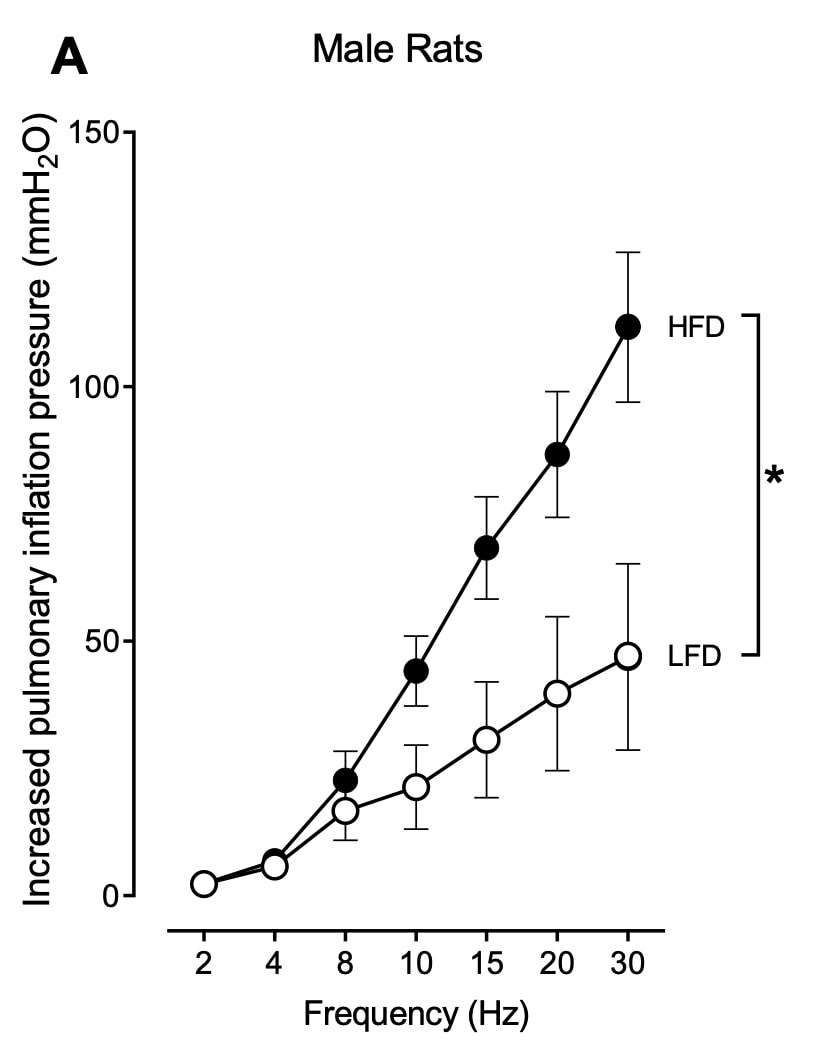
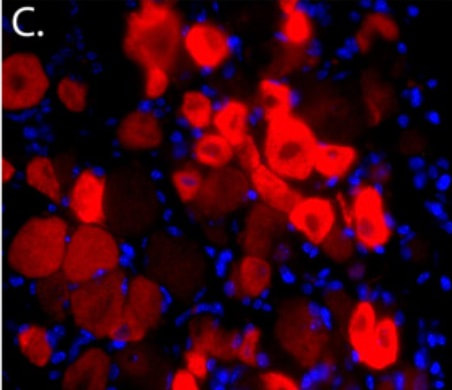
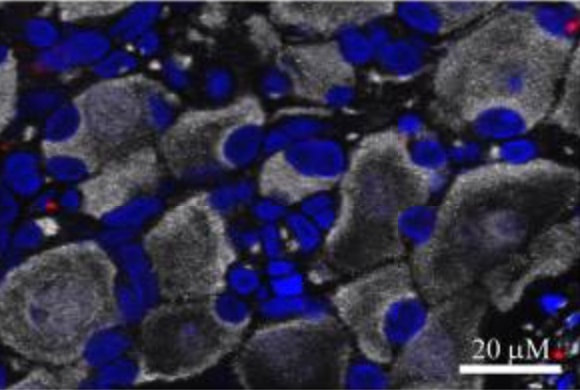
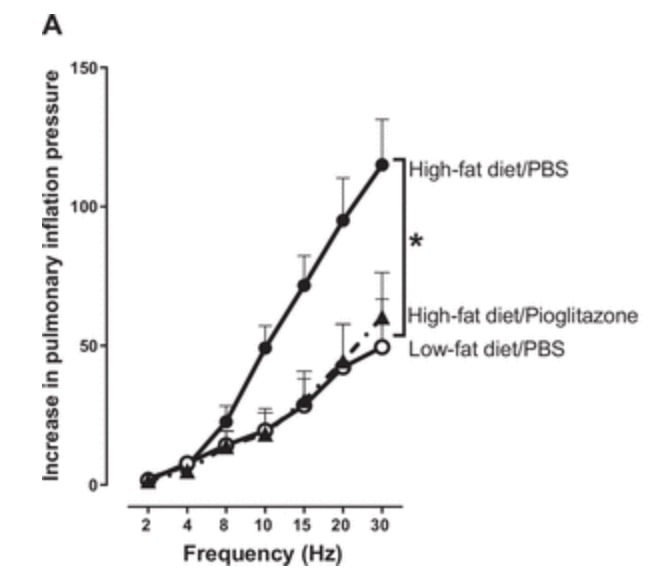
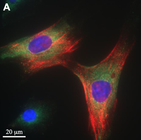
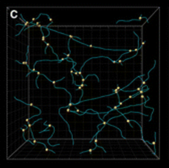
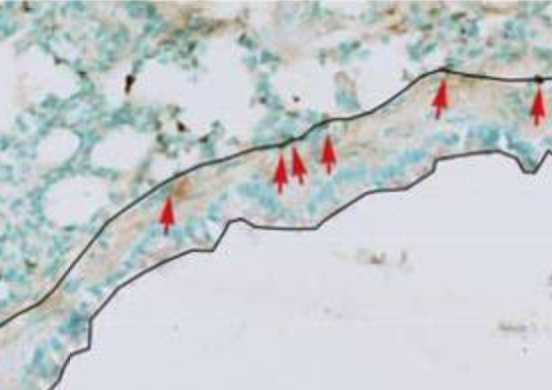
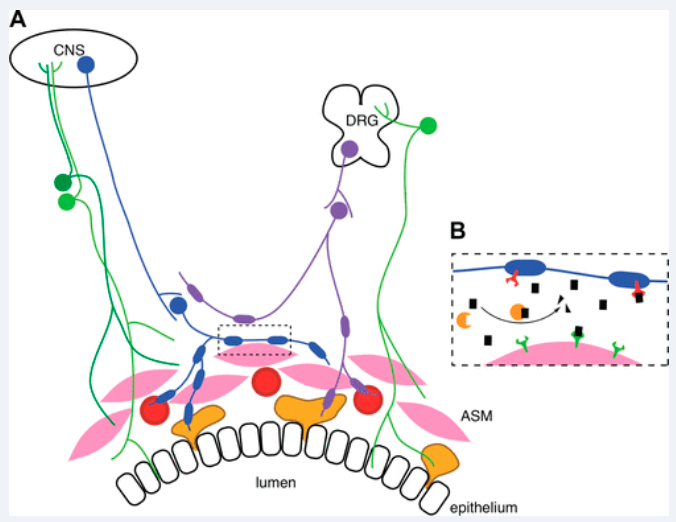
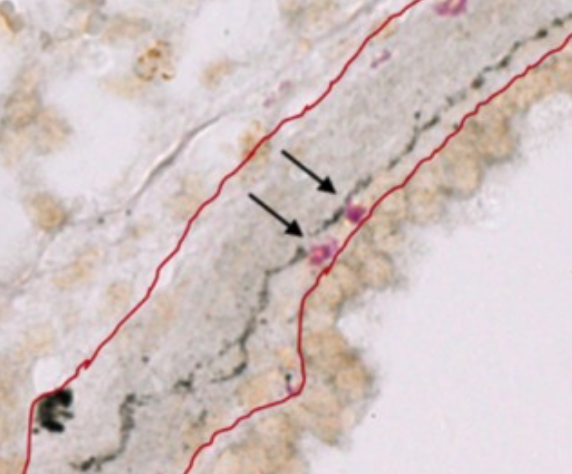
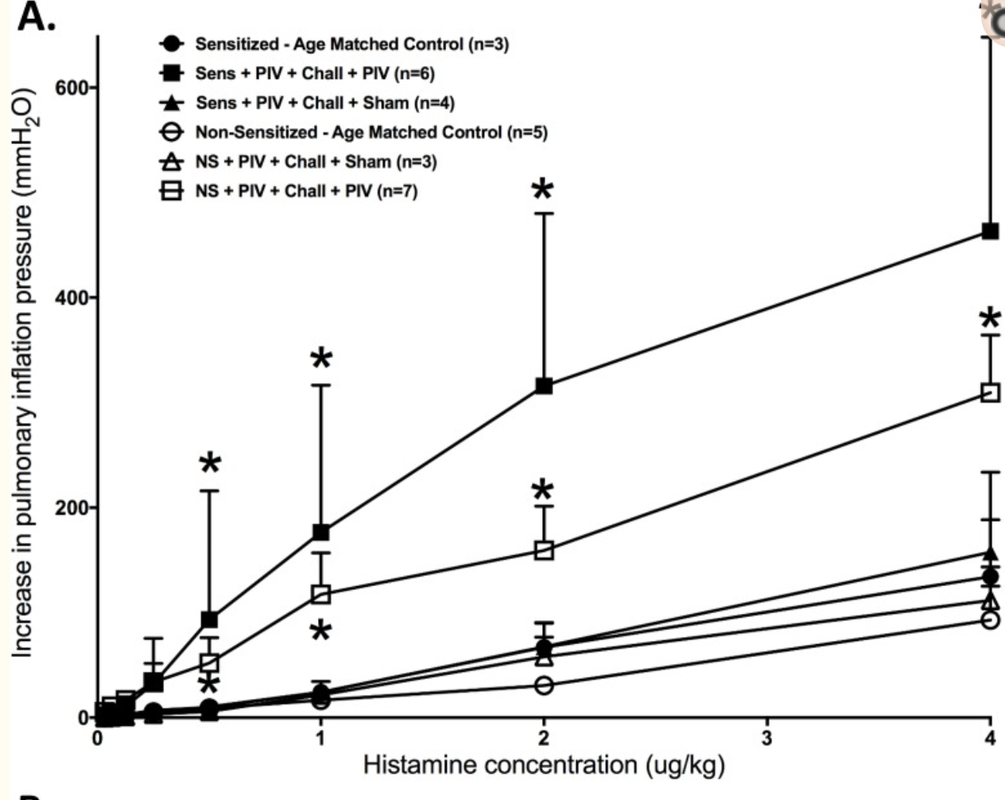
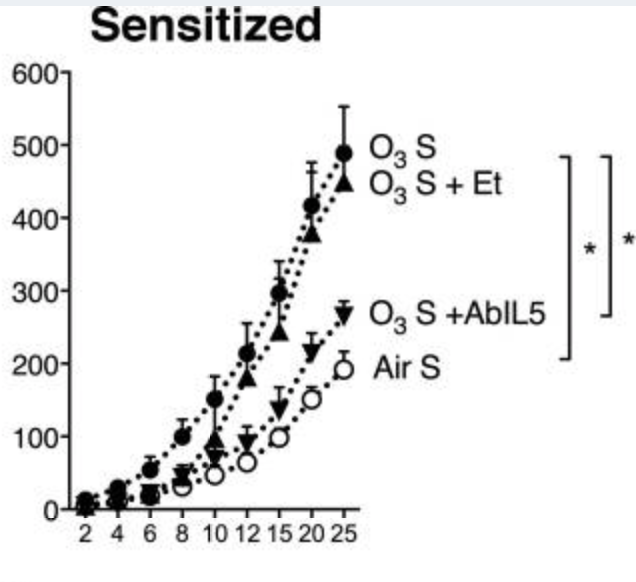
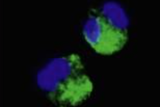
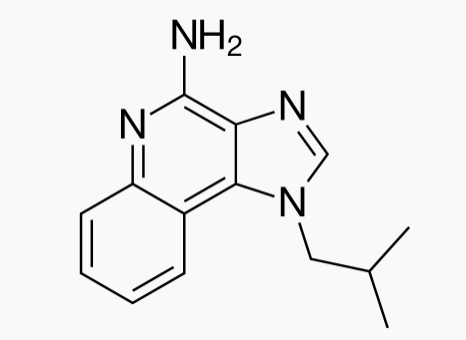
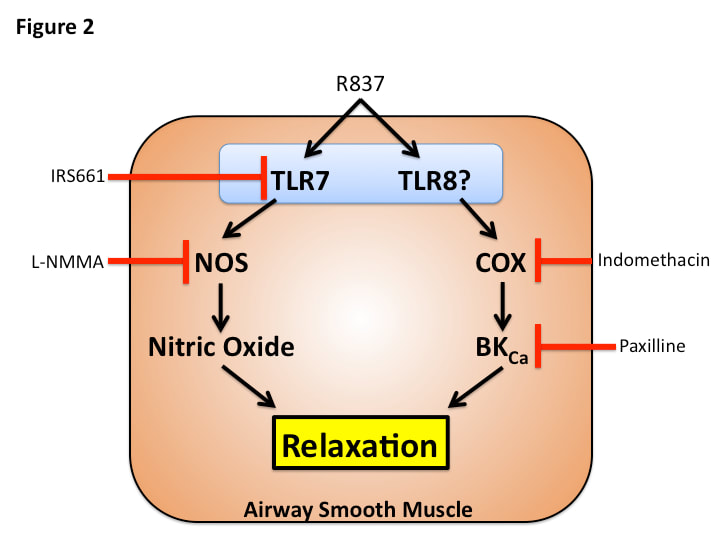
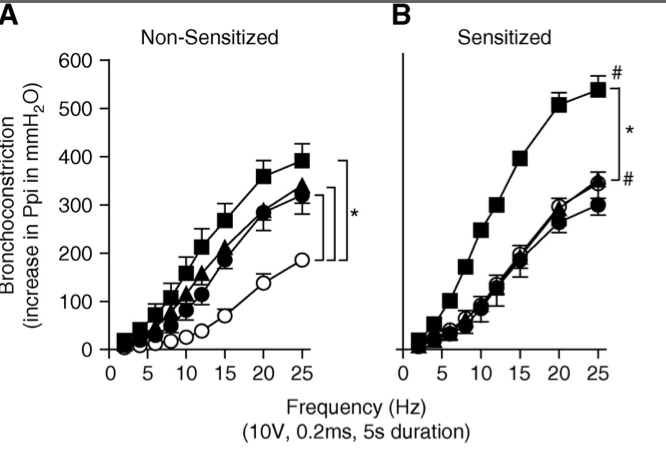
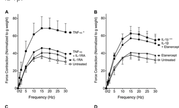
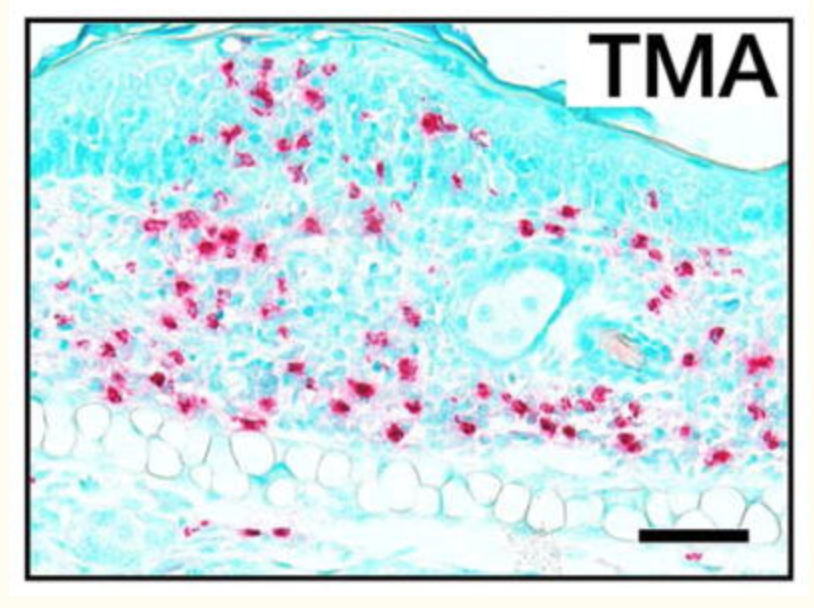
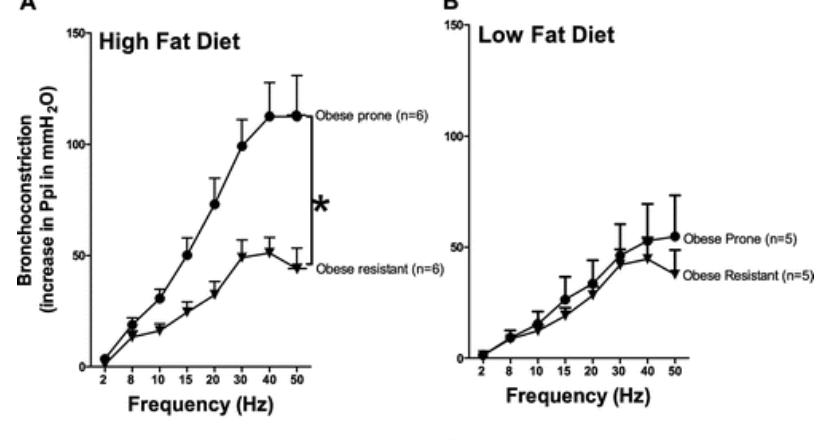
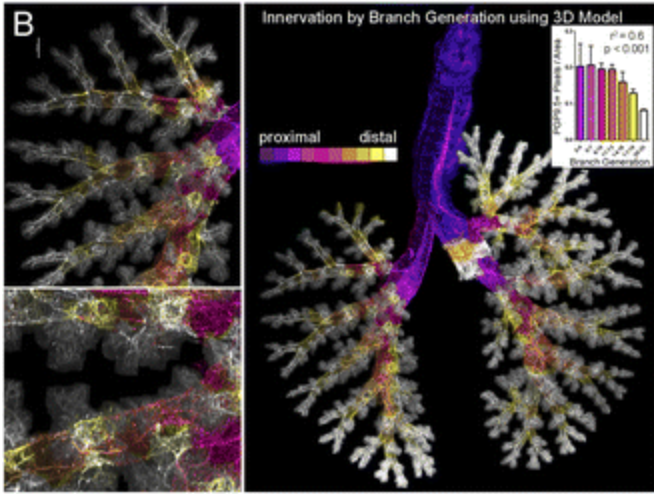
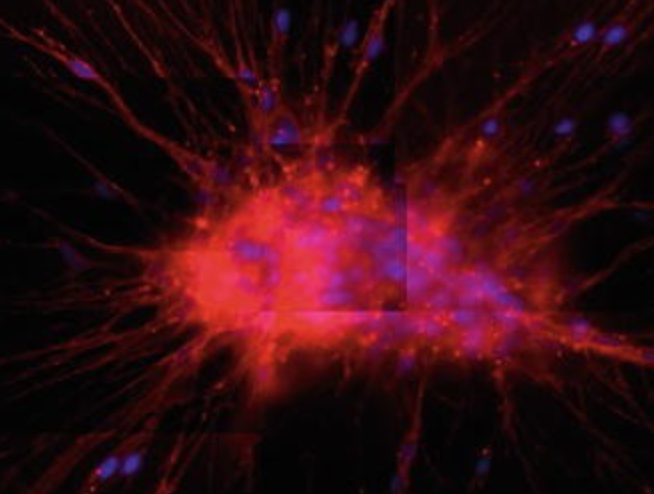
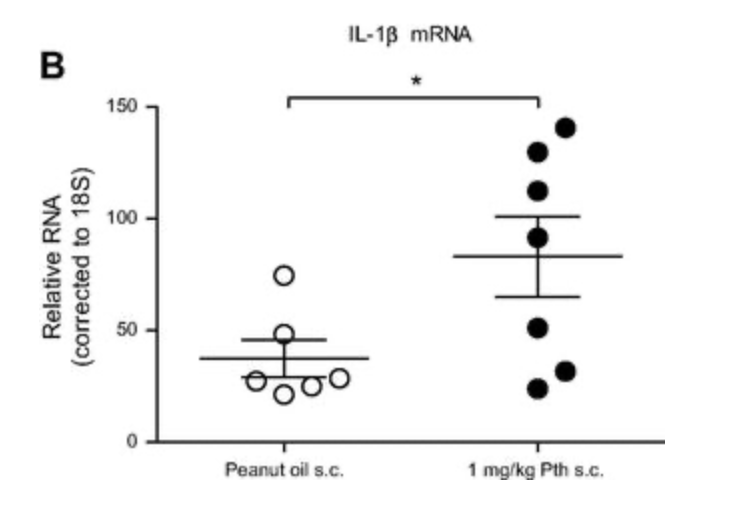
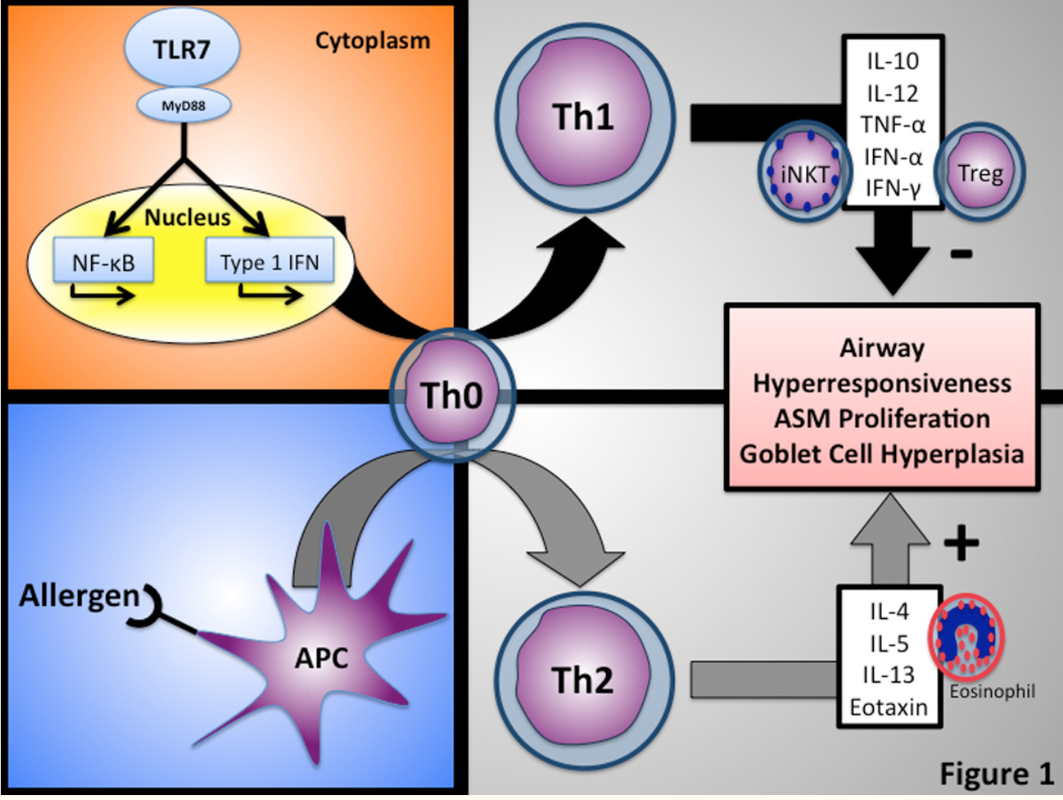
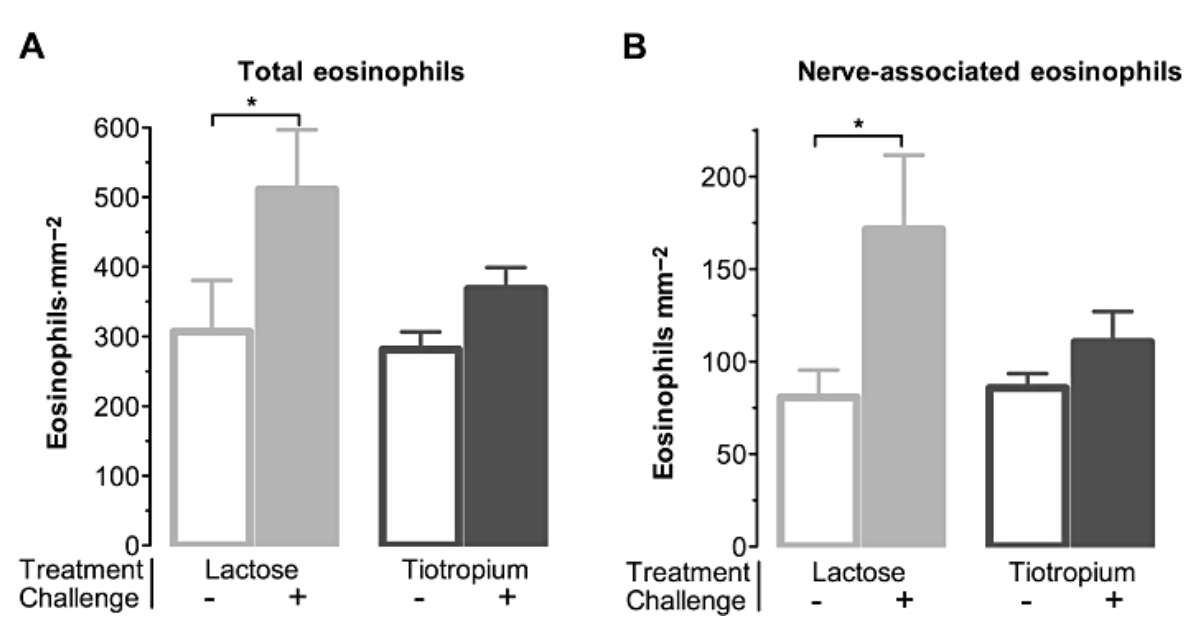
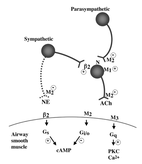
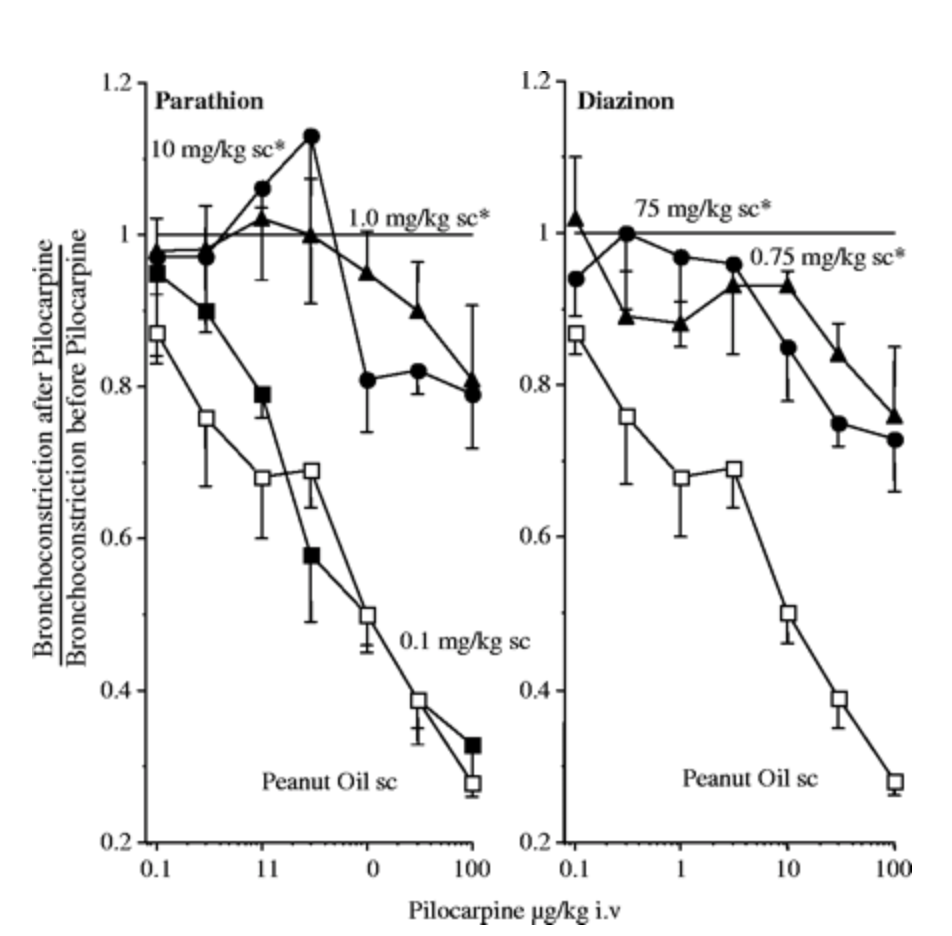
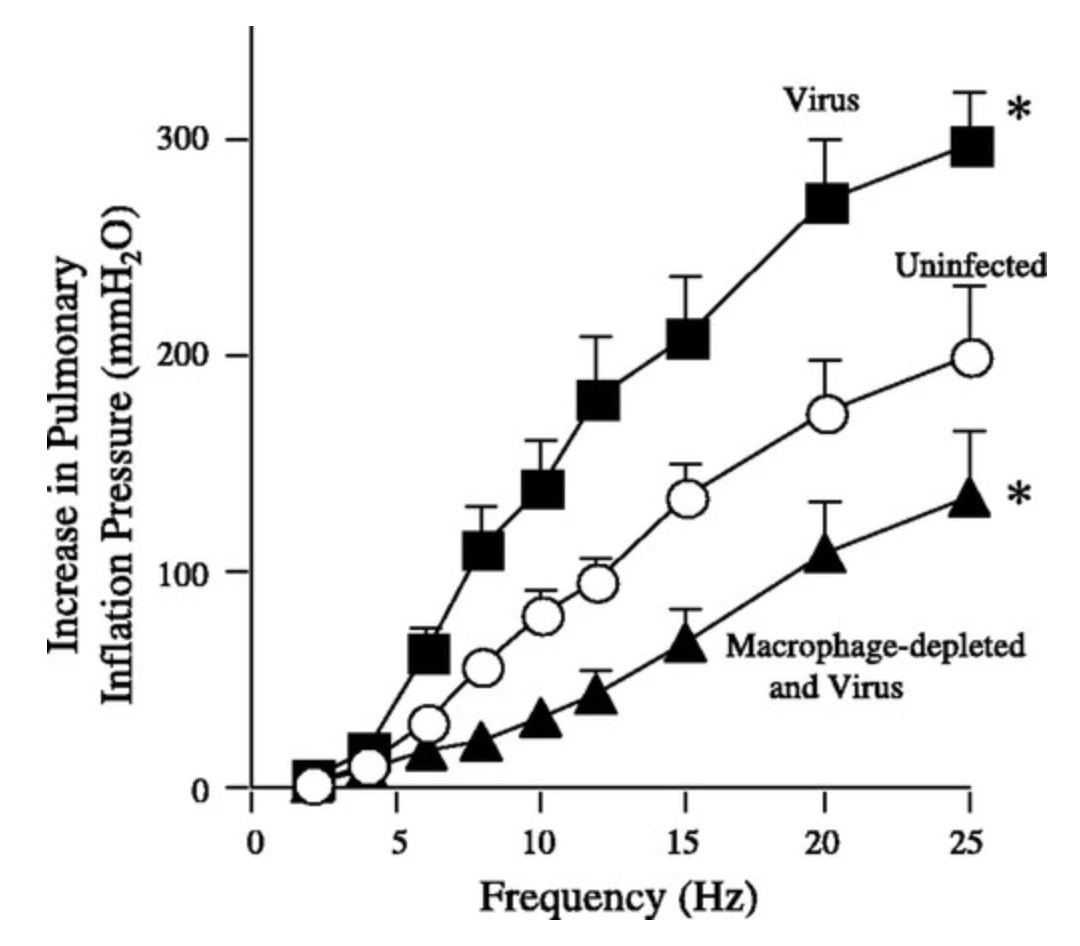
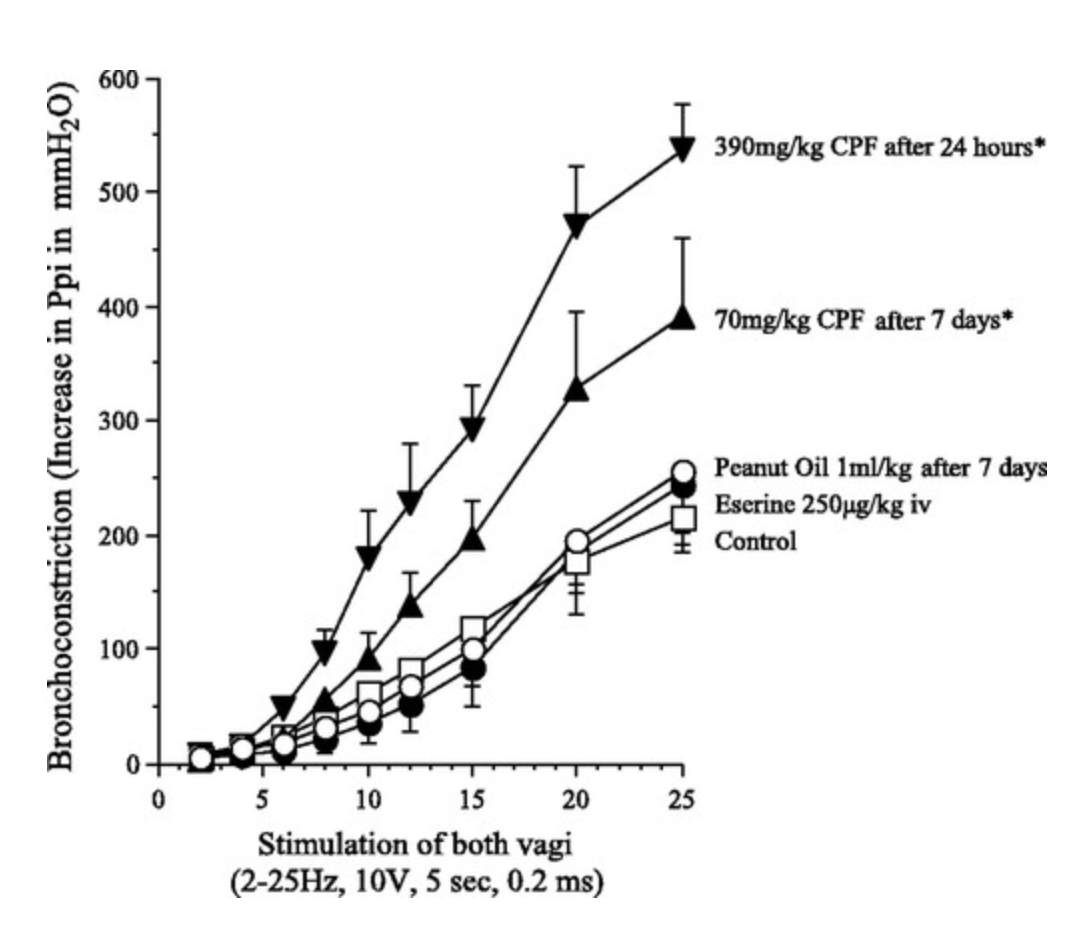
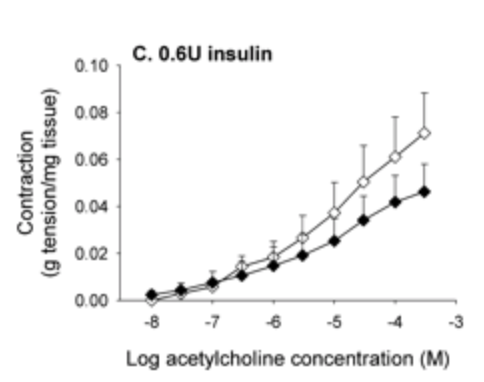
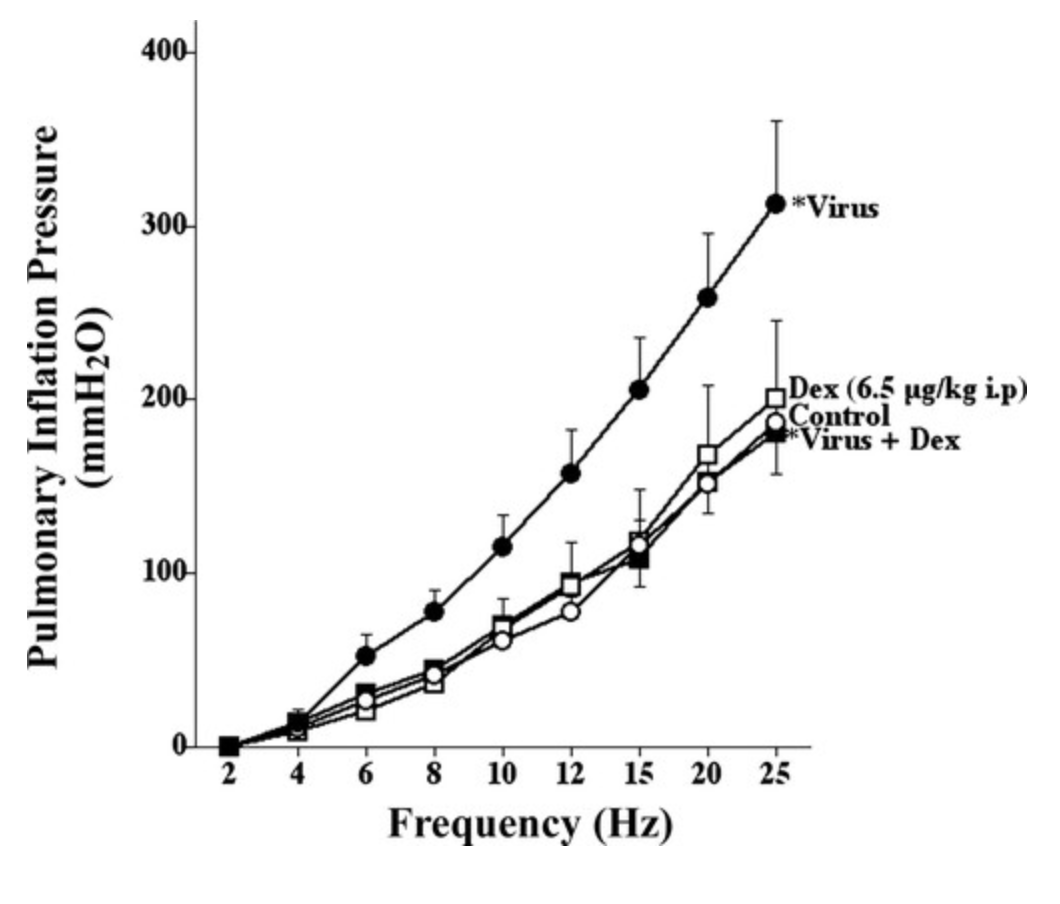
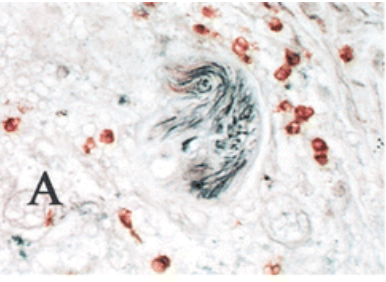
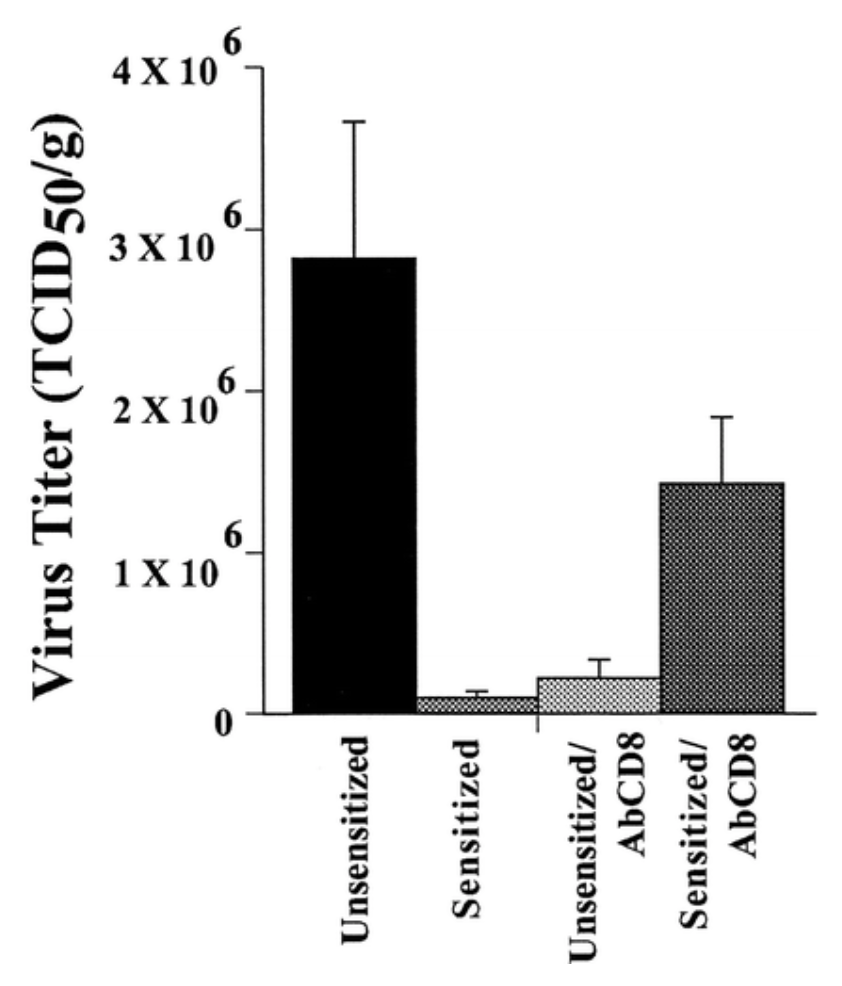
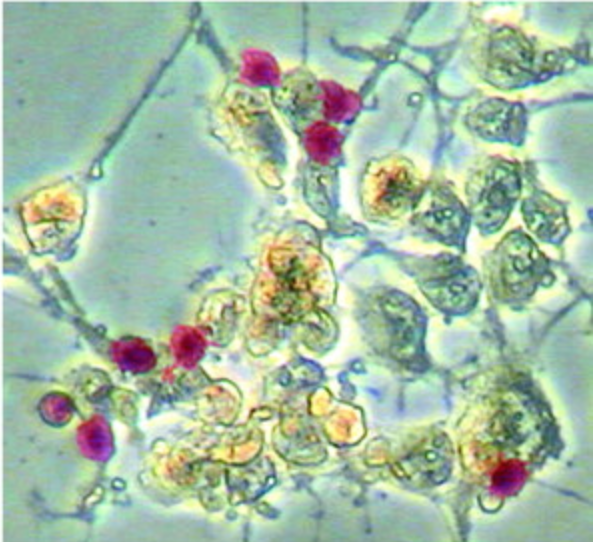
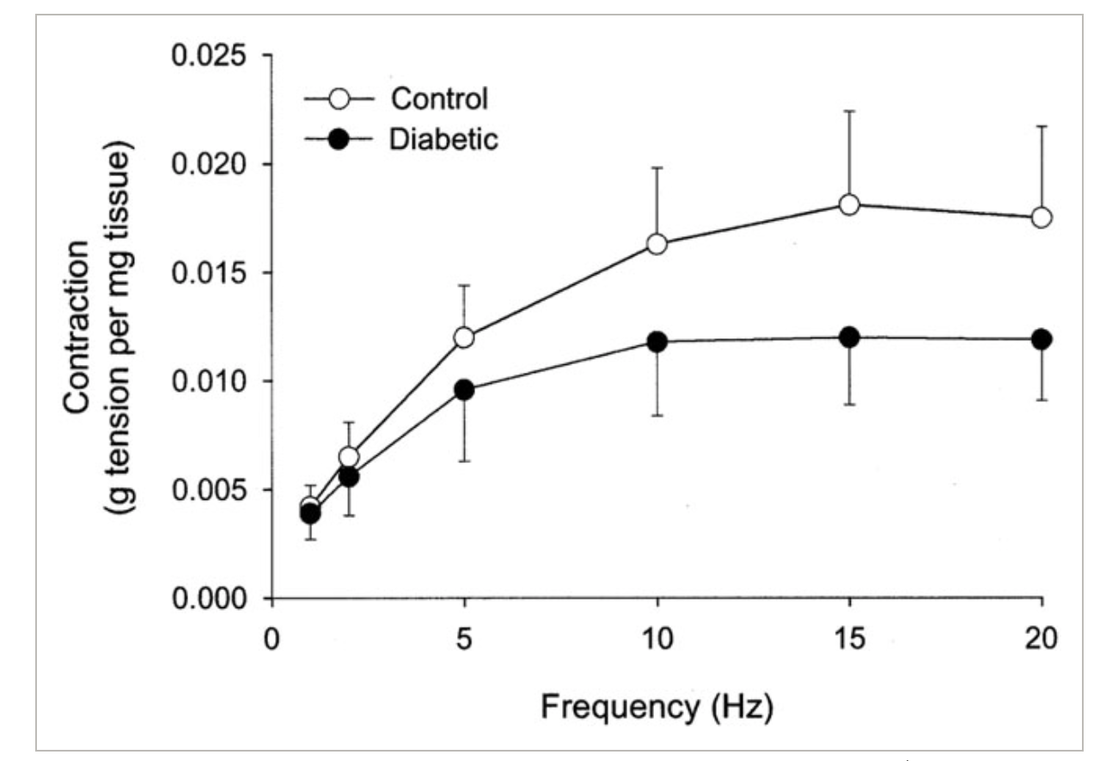
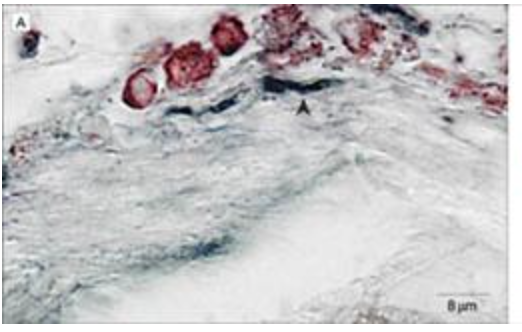
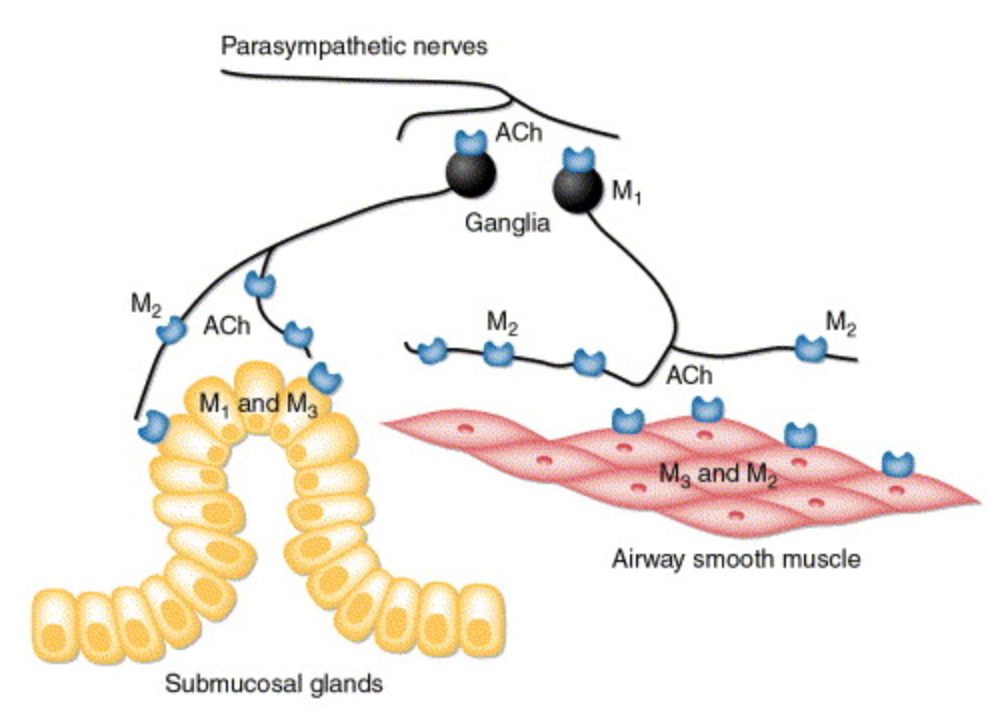
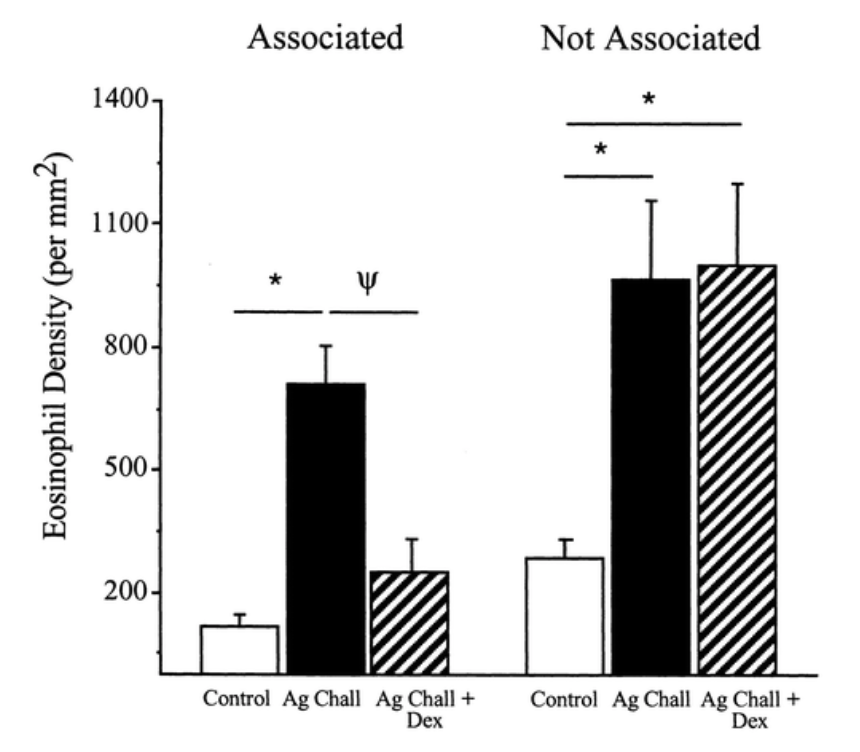
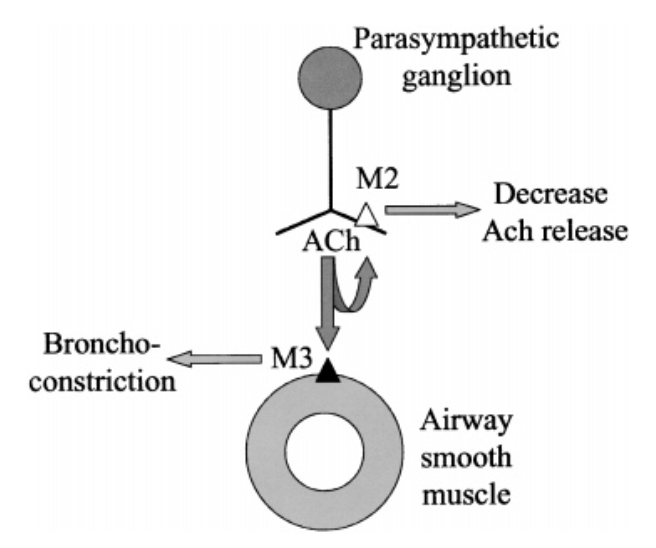
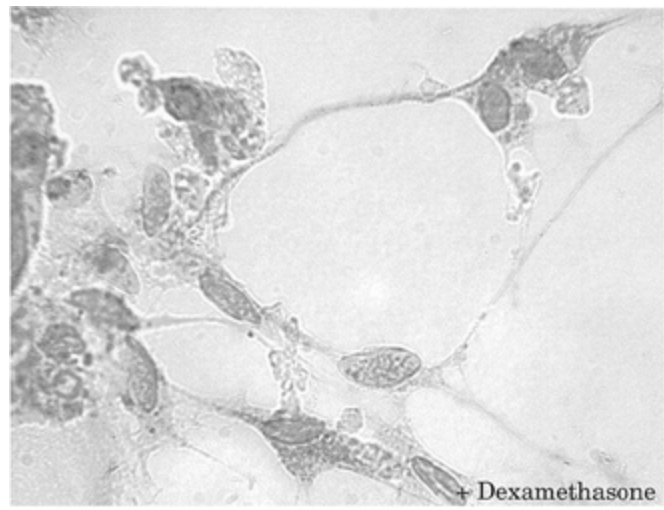
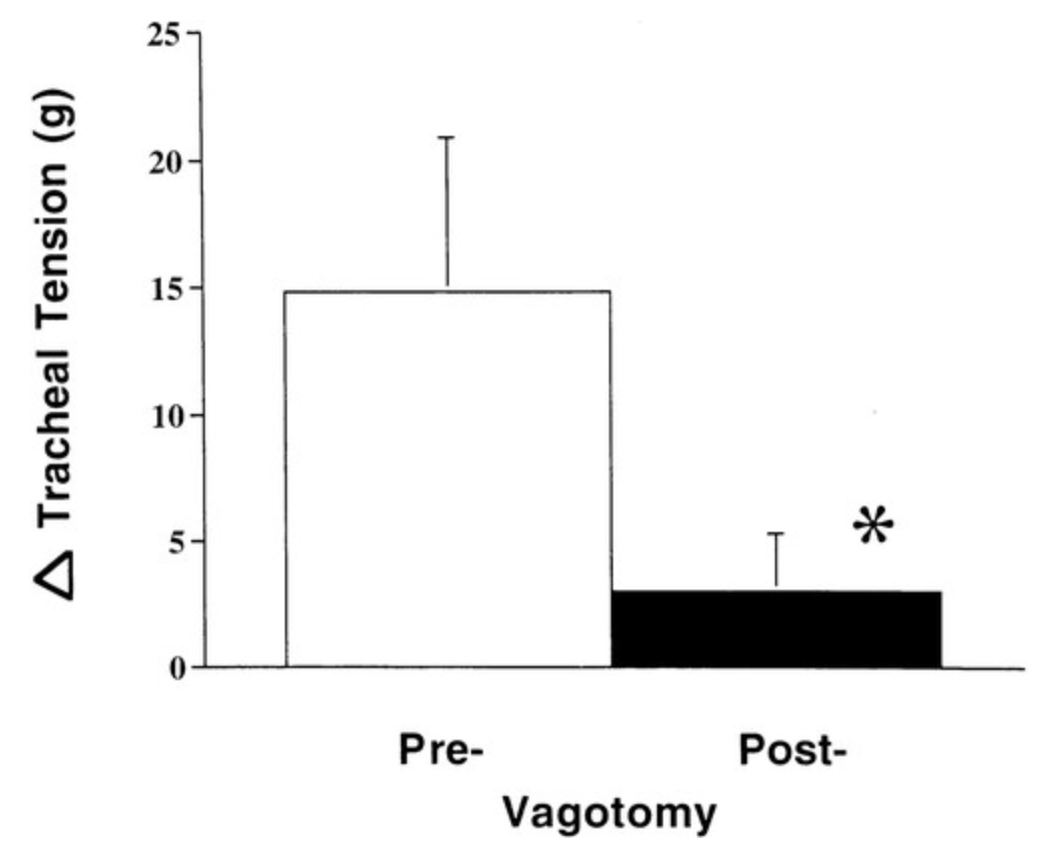
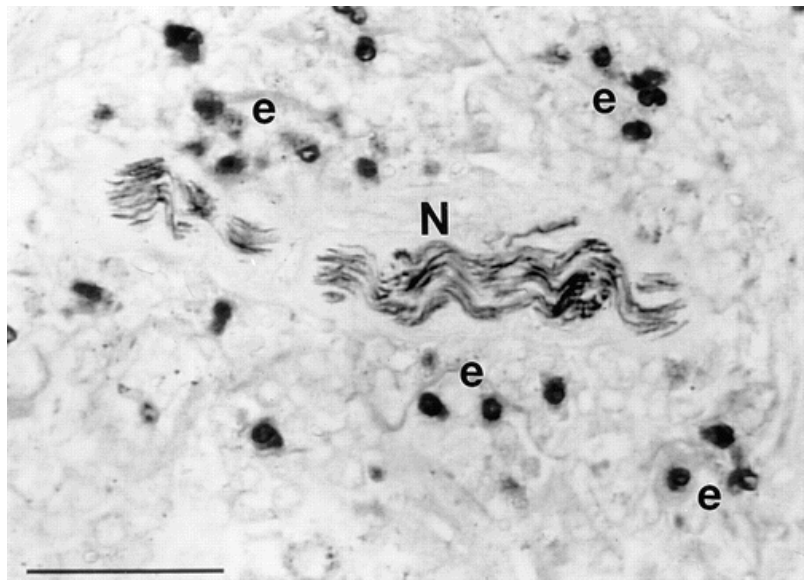
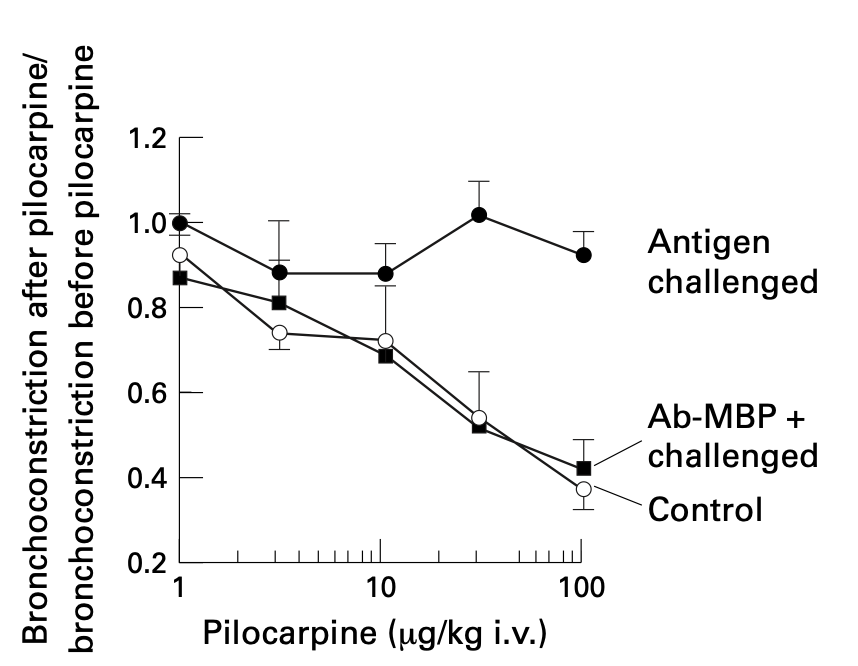
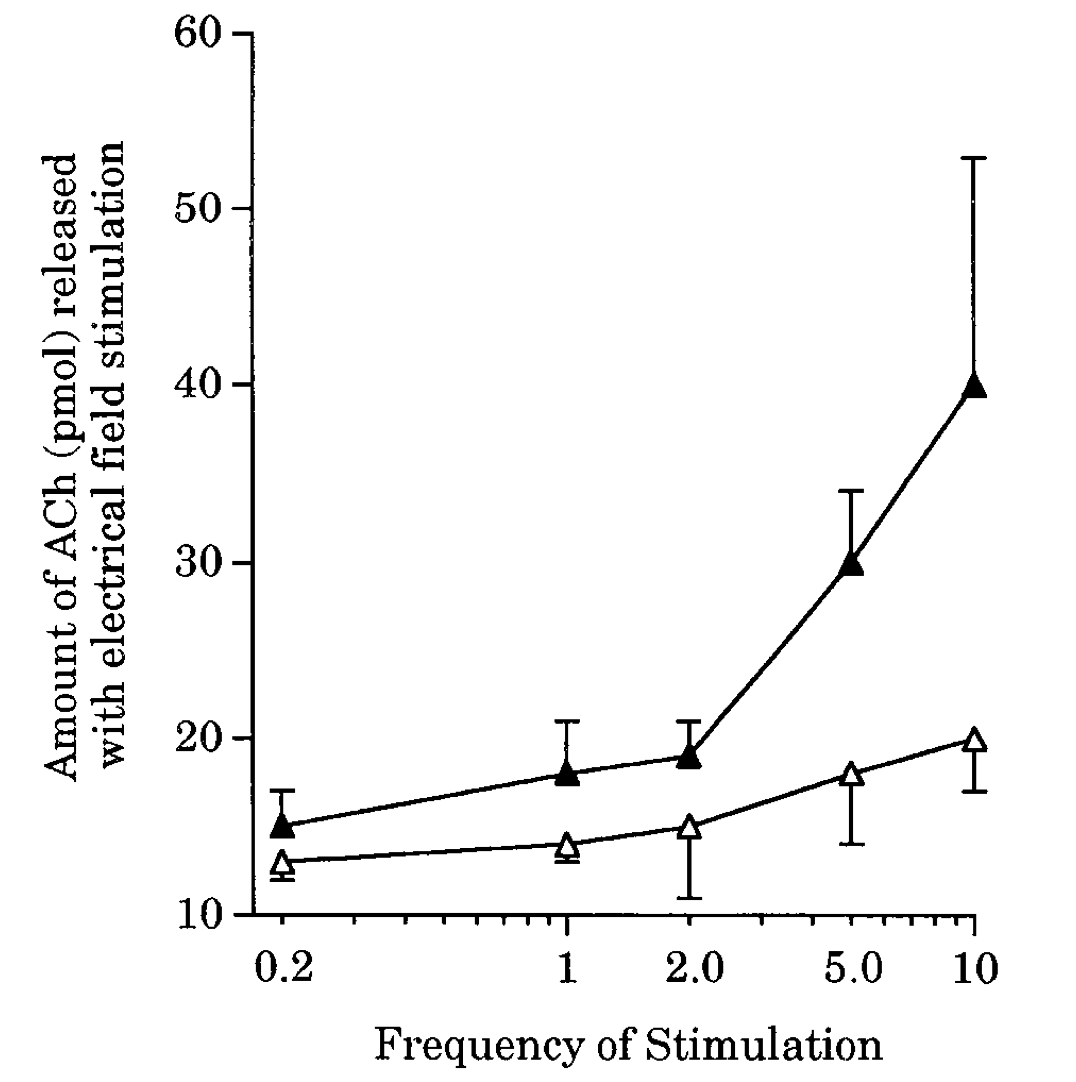
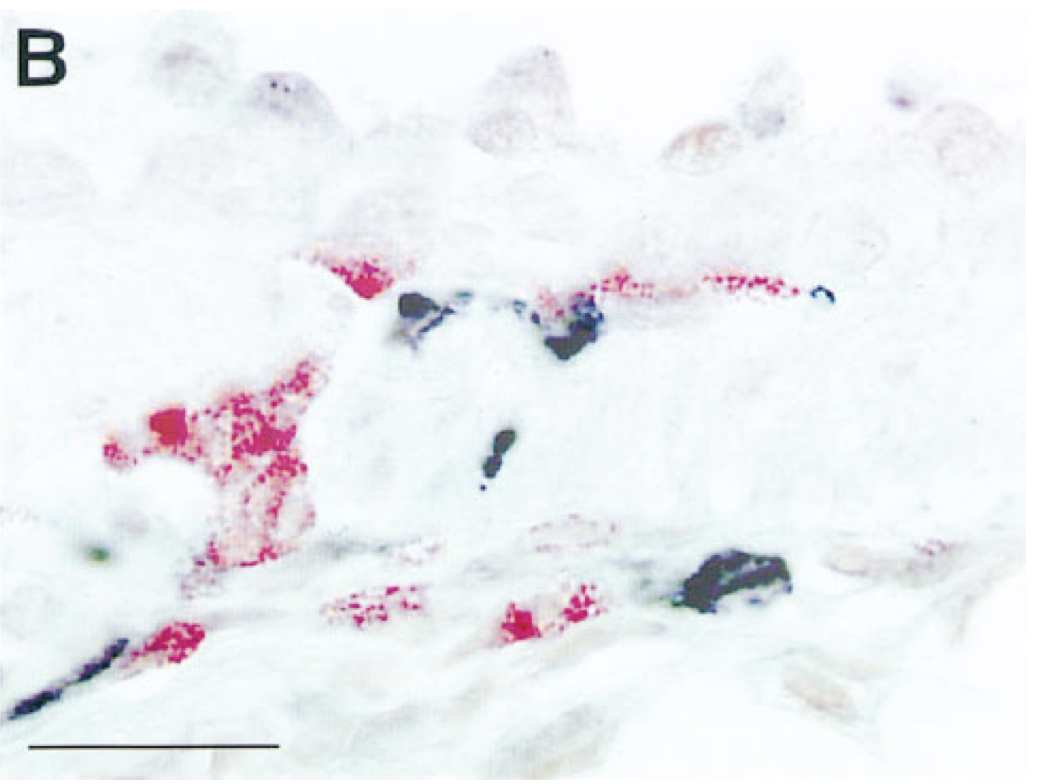
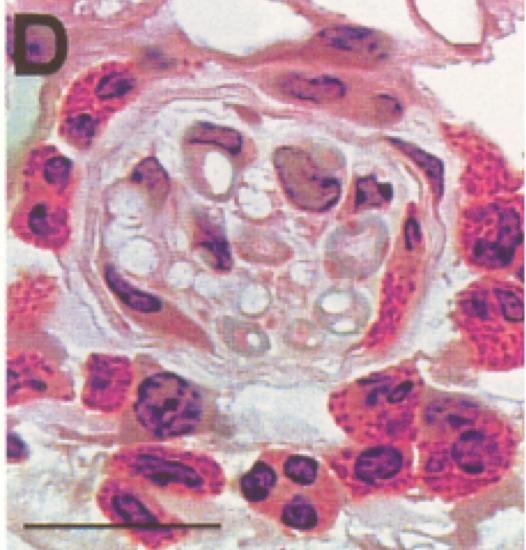
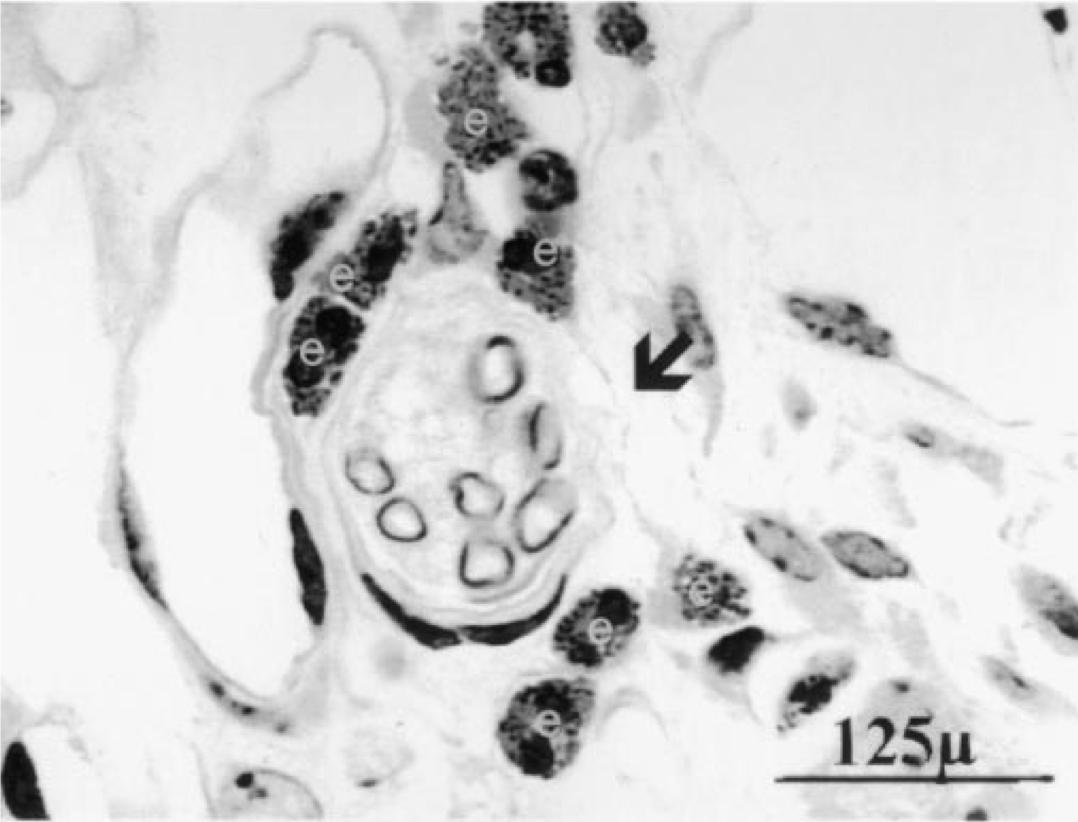
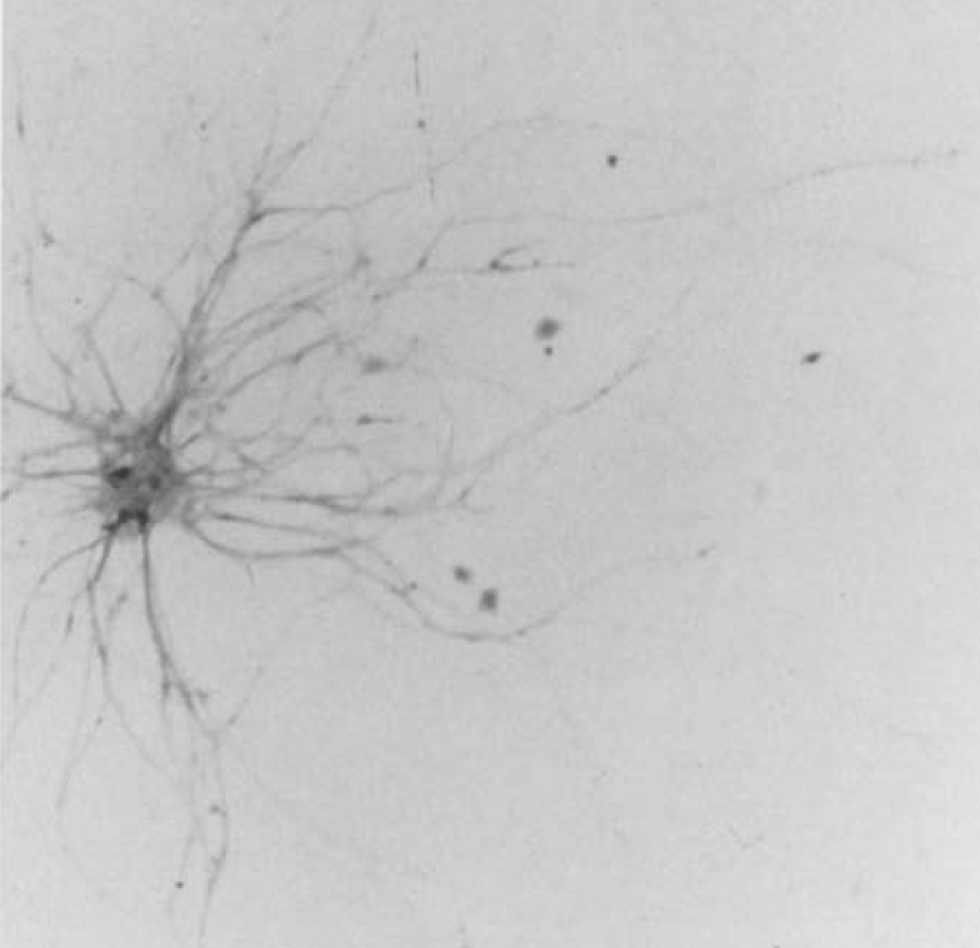
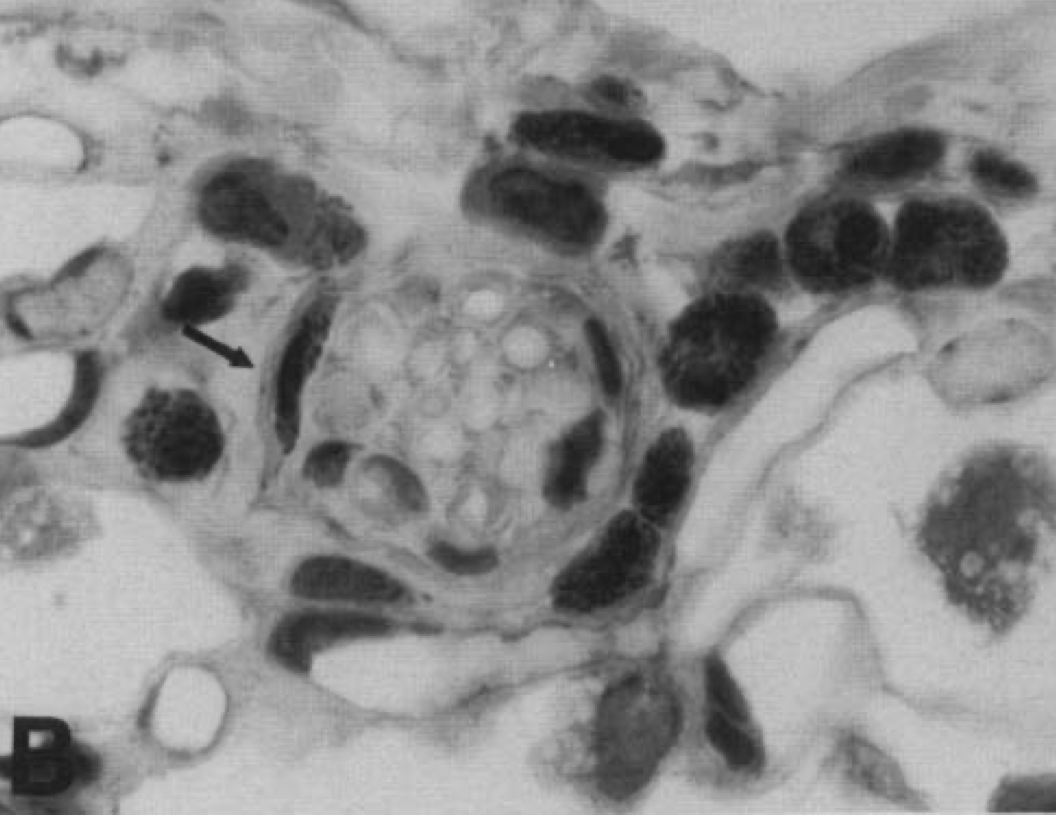
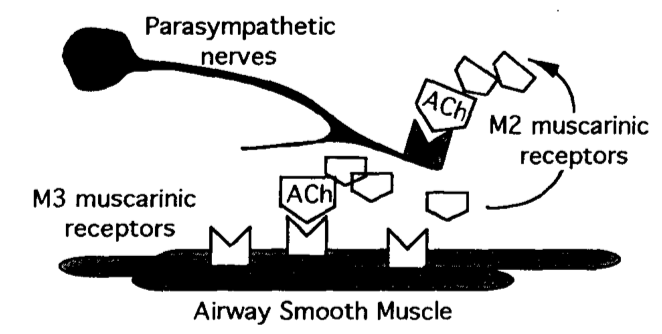
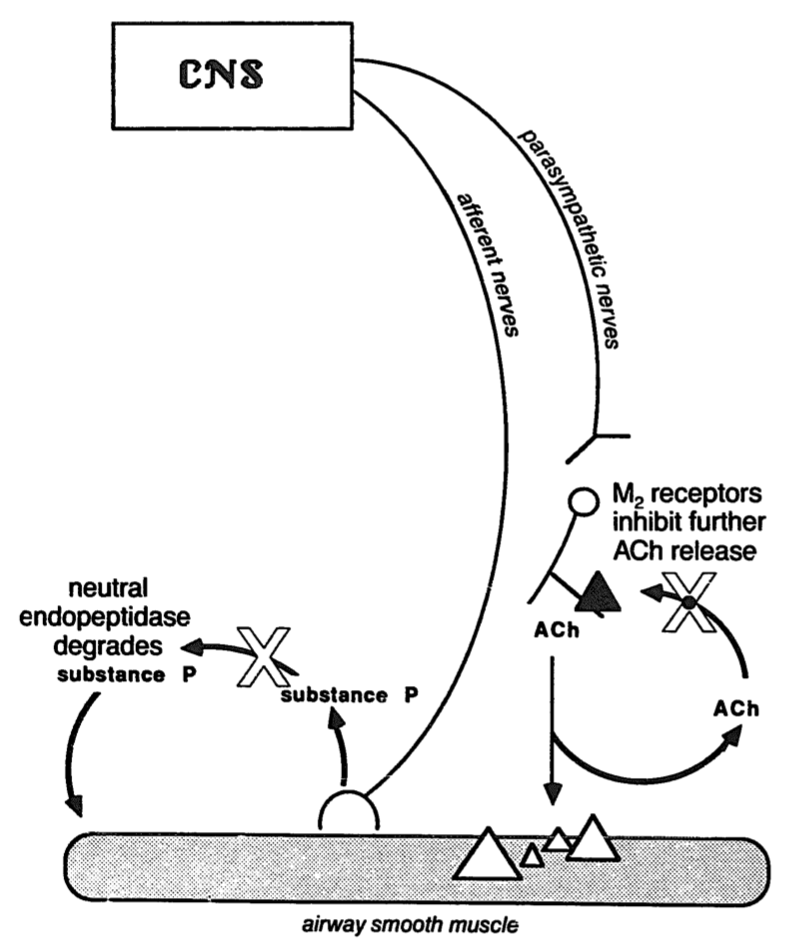
Insulin increases sensory nerve density and reflex bronchoconstriction in obese mice.
|
Unique Allergic Asthma Phenotypes in Offspring of House Dust Mite Exposed Mice.
|
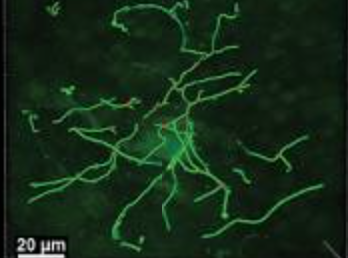
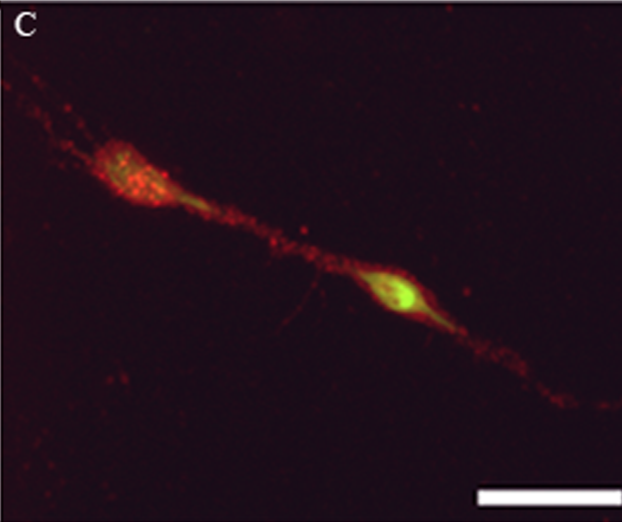
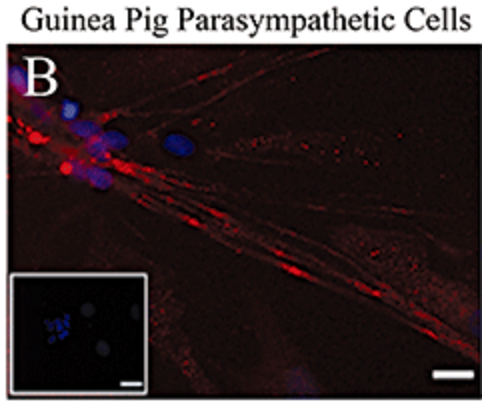
Multicolor labeling of airway neurons and analysis of parasympathetic heterogeneity.
|
Metformin prevents airway hyperreactivity in rats with dietary obesity.
|
Airway Sensory Nerve Plasticity in Asthma and Chronic Cough.
|
Eosinophils in Health and Disease: A State-of-the-Art Review.
|
TLR7 is expressed by support cells, but not sensory neurons, in ganglia.
|
Pioglitazone prevents obesity-related airway hyperreactivity and neuronal M2 receptor dysfunction.
|
Insulin acutely increases agonist-induced airway smooth muscle contraction in humans and rats.
|
Mini review: Neural mechanisms underlying airway hyperresponsiveness.
|
Airway Sensory Nerve Density Is Increased in Chronic Cough.
|
Interactions of Eosinophils with Nerves.
|
Unraveling the connection between eosinophils and obesity.
|
|
Transient receptor potential ankyrin-1 causes rapid bronchodilation via nonepithelial PGE2.
|
Optogenetic Control of Airway Cholinergic Neurons In Vivo.
|
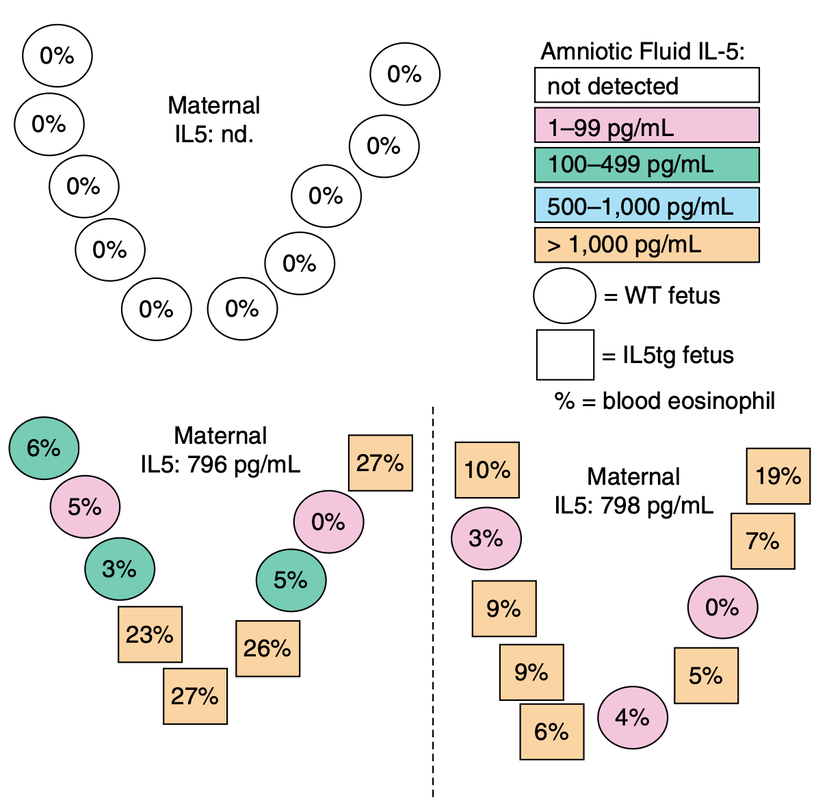
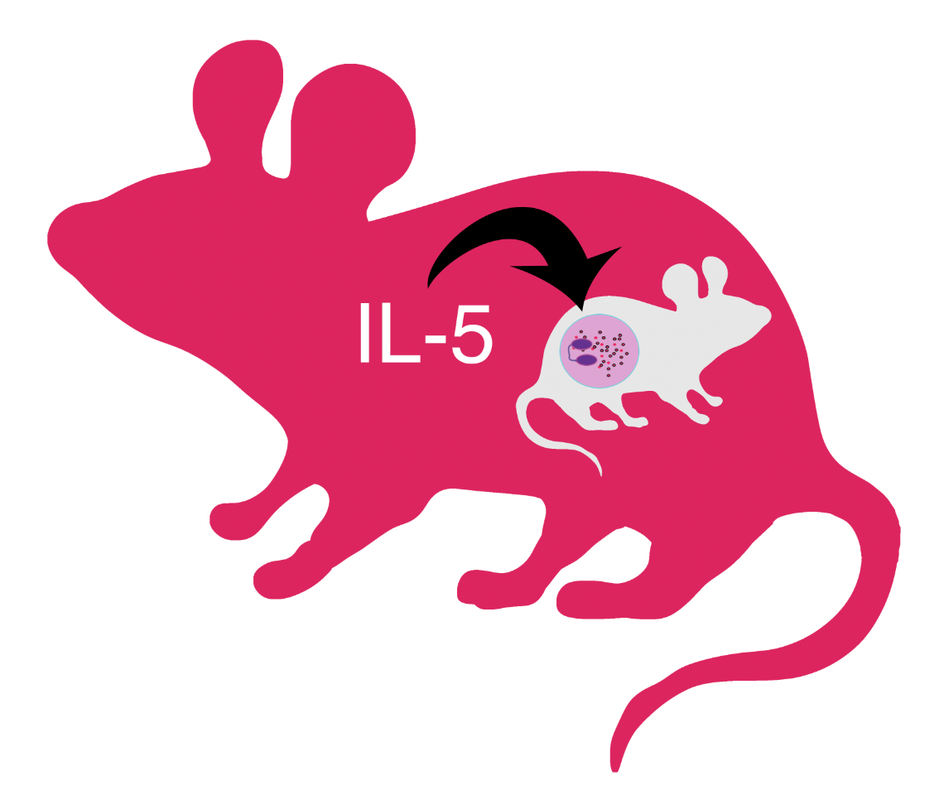
IL-5 Exposure In Utero Increases Lung Nerve Density and Airway Reactivity in Adult Offspring.
|
Inflammatory mechanisms linking maternal and childhood asthma.
|
Lung eosinophils increase vagus nerve-mediated airway reflex bronchoconstriction in mice.
|
Organophosphorus Pesticides Induce Cytokine Release from Differentiated Human THP1 Cells.
|
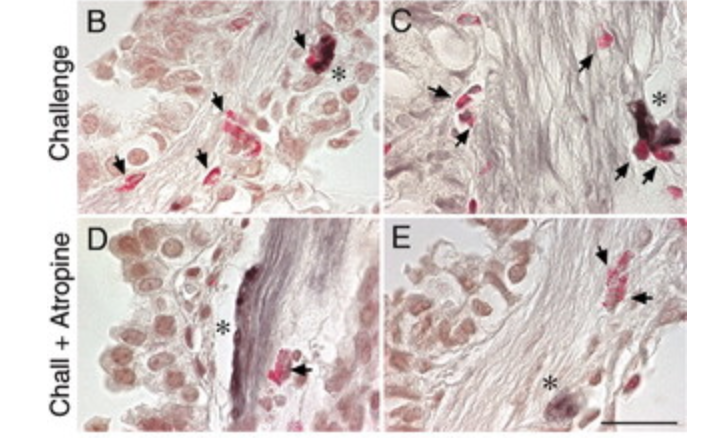
Eosinophils increase airway sensory nerve density in mice and in human asthma.
|
Eosinophil and airway nerve interactions in asthma.
|
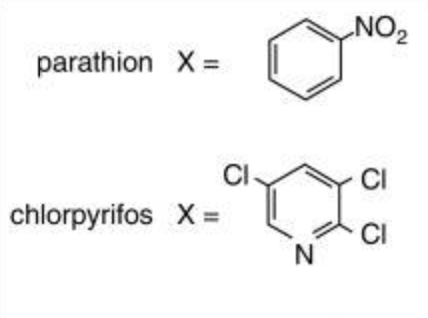
Mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide toxicity in the context of airway hyperreactivity and asthma.
|
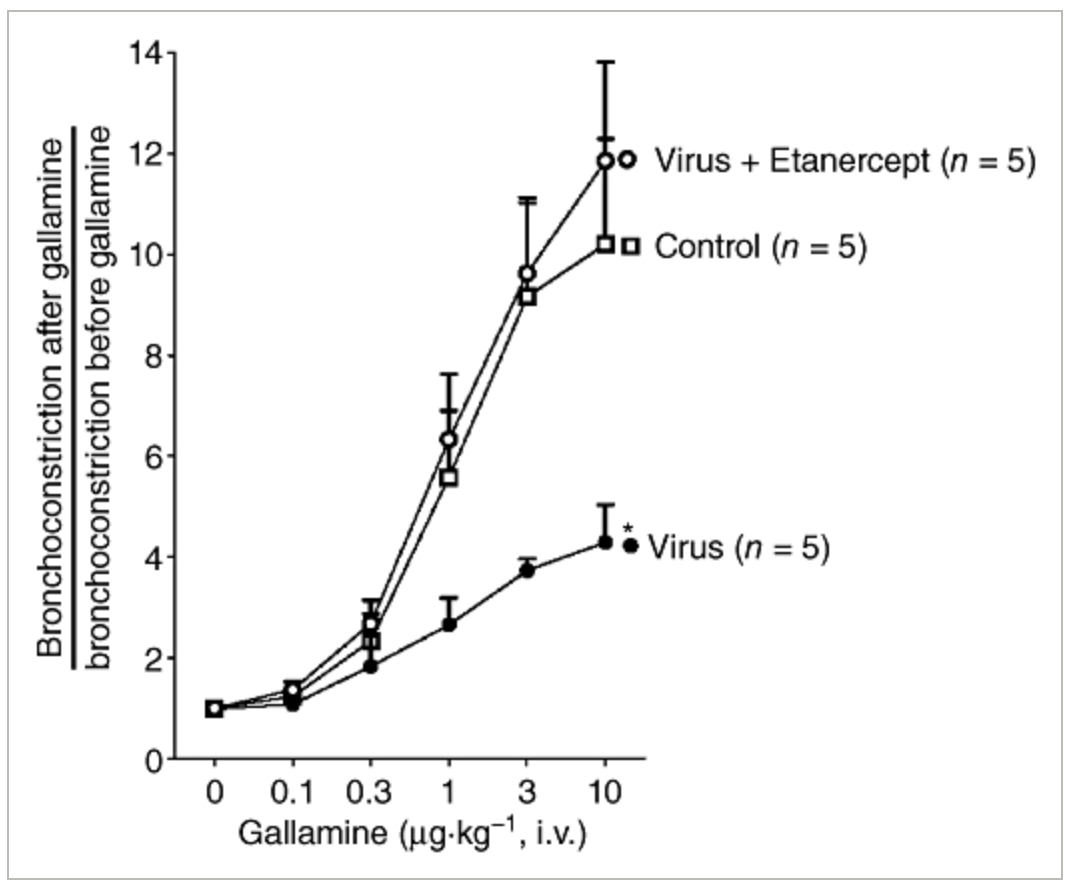
Ozone-induced eosinophil recruitment to airways is altered by antigen sensitization and tumor necrosis factor-α blockade.
|
Virus-induced asthma attack: The importance of allergic inflammation in response to viral antigen in an animal model of asthma.
|
Newly divided eosinophils limit ozone-induced airway hyperreactivity in nonsensitized guinea pigs.
|
Protective Role of Eosinophils and TNFa after Ozone Inhalation.
|
Human and Mouse Eosinophils Have Antiviral Activity against Parainfluenza Virus.
|
TLR7 agonist-induced bronchodilation: key mechanistic questions remain.
|
Toll-Like Receptor 7-Targeted Therapy in Respiratory Disease.
|
The influence of sensitization on mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide-induced airway hyperreactivity.
|
Interleukin-1β mediates virus-induced m2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction and airway hyperreactivity.
|
Eosinophil-dependent skin innervation and itching following contact toxicant exposure in mice.
|
Hyperinsulinemia potentiates airway responsiveness to parasympathetic nerve stimulation in obese rats.
|
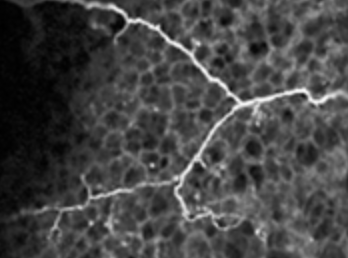
Tissue optical clearing, three-dimensional imaging, and computer morphometry in whole mouse lungs and human airways.
|
Interactions of eosinophils with nerves.
|
Dual p38/JNK mitogen activated protein kinase inhibitors prevent ozone-induced airway hyperreactivity in guinea pigs.
|
Toll-like receptor 7 rapidly relaxes human airways.
|
Toll-like receptor-2/6 and Toll-like receptor-9 agonists suppress viral replication but not airway hyperreactivity in guinea pigs.
|
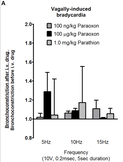
Macrophage TNF-α mediates parathion-induced airway hyperreactivity in guinea pigs.
|
The therapeutic potential of Toll-like receptor 7 stimulation in asthma.
|
Quantifying nerve architecture in murine and human airways using three-dimensional computational mapping.
|
Non-bronchodilating mechanisms of tiotropium prevent airway hyperreactivity in a guinea-pig model of allergic asthma.
|
β2-Agonists inhibit TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression in human airway parasympathetic neurons.
|
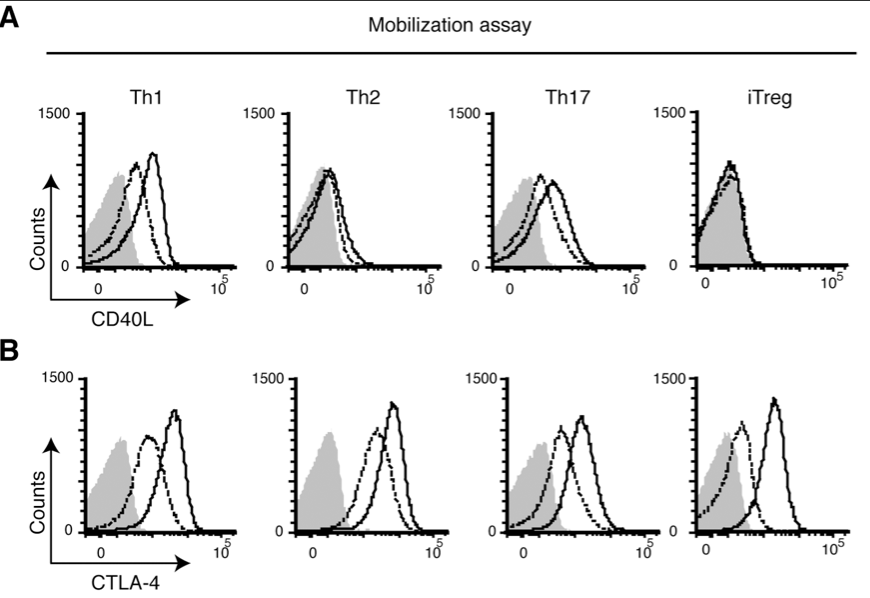
Preformed CD40L is stored in Th1, Th2, Th17, and T follicular helper cells as well as CD4+ 8- thymocytes and invariant NKT cells but not in Treg cells.
|
Role of parasympathetic nerves and muscarinic receptors in allergy and asthma.
|
Muscarinic receptor agonists and antagonists: effects on inflammation and immunity.
|
Role of TNF-α in virus-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and neuronal M₂ muscarinic receptor dysfunction.
|
Eosinophils increase neuron branching in human and murine skin and in vitro.
|
Toll-like receptor 7 agonists are potent and rapid bronchodilators in guinea pigs.
|
Three days after a single exposure to ozone, the mechanism of airway hyperreactivity is dependent on substance P and nerve growth factor.
|
Human mucosal associated invariant T cells detect bacterially infected cells.
|
Organophosphorus pesticides decrease M2 muscarinic receptor function in guinea pig airway nerves via indirect mechanisms.
|
2000 - 2009
Neural control of airway inflammation.
Verhein KC, Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009 Nov;9(6):484-90. PMID: 19814922
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19814922/
Retinoic acid prevents virus-induced airway hyperreactivity and M2 receptor dysfunction via anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects.
Moreno-Vinasco L, Verbout NG, Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):L340-6. PMID: 19465517
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19465517/
Atropine-enhanced, antigen challenge-induced airway hyperreactivity in guinea pigs is mediated by eosinophils and nerve growth factor.
|
Etanercept prevents airway hyperresponsiveness by protecting neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pigs.
|
Characterization of side population cells from human airway epithelium.
|
IL-1 receptors mediate persistent, but not acute, airway hyperreactivity to ozone in guinea pigs.
Verhein KC, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Dec;39(6):730-8. PMID: 18617681
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18617681/
Antigen sensitization influences organophosphorus pesticide-induced airway hyperreactivity.
Proskocil BJ, Bruun DA, Lorton JK, Blensly KC, Jacoby DB, Lein PJ, Fryer AD.Environ Health Perspect. 2008 Mar;116(3):381-8. PMID: 18335107
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18335107/
Expression and regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on airway parasympathetic nerves.
|
Atropine pretreatment enhances airway hyperreactivity in antigen-challenged guinea pigs through an eosinophil-dependent mechanism.
|
Neuronal eotaxin and the effects of CCR3 antagonist on airway hyperreactivity and M2 receptor dysfunction.
|
The changing role of eosinophils in long-term hyperreactivity following a single ozone exposure.
|
Beta2-agonist and anticholinergic drugs in the treatment of lung disease.
|
Organophosphorus insecticides induce airway hyperreactivity by decreasing neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function independent of acetylcholinesterase inhibition.
|
Virus-induced asthma attacks.
Jacoby DB. J Aerosol Med. 2004 Summer;17(2):169-73. PMID: 15294068
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15294068/
Role of macrophages in virus-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction.
|
Mechanisms of organophosphate insecticide-induced airway hyperreactivity.
|
Pathophysiology of airway viral infections.
Jacoby DB. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2004;17(6):333-6. PMID: 15564071
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15564071/
Insulin regulates neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function in the ileum of diabetic rats.
|
Effects of eosinophils on nerve cell morphology and development: the role of reactive oxygen species and p38 MAP kinase.
|
Dexamethasone prevents virus-induced hyperresponsiveness via multiple mechanisms.
|
Airway neural plasticity: the nerves they are a-changin'.
|
Plasticity of cholinergic and tachykinergic nerves: the convergence of the twain.
Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002 Nov;283(5):L907-8. PMID: 12376342
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12376342/
CD8+ T lymphocytes in viral hyperreactivity and M2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction.
|
Eosinophil adhesion to cholinergic nerves via ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 and associated eosinophil degranulation.
|
Expression of tachykinins in nonnociceptive vagal afferent neurons during respiratory viral infection in guinea pigs.
Carr MJ, Hunter DD, Jacoby DB, Undem BJ. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Apr 15;165(8):1071-5. PMID: 11956047
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11956047/
Double-stranded RNA causes airway hyperreactivity and neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction.
Bowerfind WM, Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002 Apr;92(4):1417-22. PMID: 11896005
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11896005/
Increased function of inhibitory neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in trachea and ileum of diabetic rats.
|
Virus-induced asthma attacks.
|
Structure of the human M(2) muscarinic acetylcholine receptor gene and its promoter.
Zhou C, Fryer AD, Jacoby DB. Gene. 2001 Jun 13;271(1):87-92. PMID: 11410369
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11410369/
Selective muscarinic receptor antagonists for airway diseases.
|
Effects of dexamethasone on antigen-induced airway eosinophilia and M(2) receptor dysfunction.
|
Anticholinergic therapy for airway diseases.
|
Glucocorticoid treatment increases inhibitory m(2) muscarinic receptor expression and function in the airways.
|
Eosinophil recruitment to the airway nerves.
|
Substance P-induced airway hyperreactivity is mediated by neuronal M(2) receptor dysfunction.
|
Inhibition of neuronal M(2) muscarinic receptor function in the lungs by extracellular nitric oxide.
Golkar L, Yarkony KA, Fryer AD.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Sep;131(2):312-8. PMID: 10991925
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10991925/
Eosinophils and airway nerves in asthma.
Costello RW, Jacoby DB, Gleich GJ, Fryer AD. Histol Histopathol. 2000 Jul;15(3):861-8. PMID: 10963130
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10963130/
Effects of neurokinin receptor antagonists in virus-infected airways.
|
1990-1999
Ovalbumin sensitization changes the inflammatory response to subsequent parainfluenza infection. Eosinophils mediate airway hyperresponsiveness, m(2) muscarinic receptor dysfunction, and antiviral effects.
Adamko DJ, Yost BL, Gleich GJ, Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.J Exp Med. 1999 Nov 15;190(10):1465-78. PMID: 10562321
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10562321/
Ozone-induced hyperresponsiveness and blockade of M2 muscarinic receptors by eosinophil major basic protein.
|
Interaction of viral infections with muscarinic receptors.
Jacoby DB, Fryer AD.Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Jun;29 Suppl 2:59-64. PMID: 10421824
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10421824/
Antigen-induced hyperreactivity to histamine: role of the vagus nerves and eosinophils.
Costello RW, Evans CM, Yost BL, Belmonte KE, Gleich GJ, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD.Am J Physiol. 1999 May;276(5):L709-14. PMID: 10330026
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10330026/
Effects of inflammatory cells on neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function in the lung.
Fryer AD, Adamko DJ, Yost BL, Jacoby DB. Life Sci. 1999;64(6-7):449-55. PMID: 10069509
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10069509/
Methacholine causes reflex bronchoconstriction.
|
Muscarinic receptors and control of airway smooth muscle.
|
Role of insulin in antigen-induced airway eosinophilia and neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction.
Belmonte KE, Fryer AD, Costello RW.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1998 Nov;85(5):1708-18. PMID: 980457
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9804573/
Pulmonary neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function in asthma and animal models of hyperreactivity.
|
Virus- and interferon-induced loss of inhibitory M2 muscarinic receptor function and gene expression in cultured airway parasympathetic neurons.
|
Effects of tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonists on vagal hyperreactivity and neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function in antigen challenged guinea-pigs.
Costello RW, Fryer AD, Belmonte KE, Jacoby DB.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 May;124(2):267-76. PMID: 9641542
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9641542/
Role of oxidants in influenza virus-induced gene expression.
Knobil K, Choi AM, Weigand GW, Jacoby DB.Am J Physiol. 1998 Jan;274(1):L134-42. PMID: 9458811
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9458811/
Pretreatment with antibody to eosinophil major basic protein prevents hyperresponsiveness by protecting neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pigs.
|
Increased function of inhibitory neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in diabetic rat lungs.
Belmonte KE, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD. Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Aug;121(7):1287-94. PMID: 9257905
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9257905/
Localization of eosinophils to airway nerves and effect on neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function.
|
Antibody to VLA-4, but not to L-selectin, protects neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pig airways.
|
Role of the respiratory epithelium in asthma.
Jacoby DB. Res Immunol. 1997 Jan;148(1):48-58. PMID: 9176919
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9176919/
Cultures of airway parasympathetic nerves express functional M2 muscarinic receptors.
|
Oxidant stress responses in influenza virus pneumonia: gene expression and transcription factor activation.
Choi AM, Knobil K, Otterbein SL, Eastman DA, Jacoby DB.Am J Physiol. 1996 Sep;271(3 Pt 1):L383-91. PMID: 8843786
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8843786/
Viral infection induces dependence of neuronal M2 muscarinic receptors on cyclooxygenase in guinea pig lung.
Kahn RM, Okanlami OA, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD.J Clin Invest. 1996 Jul 15;98(2):299-307. PMID: 8755638
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8755638/
NIH conference. Airway inflammation.
Shelhamer JH, Levine SJ, Wu T, Jacoby DB, Kaliner MA, Rennard SI.Ann Intern Med. 1995 Aug 15;123(4):288-304. PMID: 7611596
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7611596/
Infection of a human respiratory epithelial cell line with rhinovirus. Induction of cytokine release and modulation of susceptibility to infection by cytokine exposure.
Subauste MC, Jacoby DB, Richards SM, Proud D. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jul;96(1):549-57. PMID: 7615827
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7615827/
Eosinophil-associated inflammation in bronchial asthma: a connection to the nervous system.
Gleich GJ, Jacoby DB, Fryer AD.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995 May-Jun;107(1-3):205-7. PMID: 7542072
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7542072/
Pretreatment with an antibody to interleukin-5 prevents loss of pulmonary M2 muscarinic receptor function in antigen-challenged guinea pigs.
|
Ozone-induced loss of neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function is prevented by cyclophosphamide.
Gambone LM, Elbon CL, Fryer AD.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1994 Sep;77(3):1492-9. PMID: 7836157
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7836157/
The effect of leukocyte depletion on pulmonary M2 muscarinic receptor function in parainfluenza virus-infected guinea-pigs.
Fryer AD, Yarkony KA, Jacoby DB.Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):588-94. PMID: 8075876
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8075876/
Influenza virus induces expression of antioxidant genes in human epithelial cells.
|
Ozone-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and loss of neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function.
Schultheis AH, Bassett DJ, Fryer AD.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1994 Mar;76(3):1088-97. PMID: 8005850
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8005850/
Human eosinophil major basic protein is an endogenous allosteric antagonist at the inhibitory muscarinic M2 receptor.
Jacoby DB, Gleich GJ, Fryer AD.J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1314-8. PMID: 8473484
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8473484/
Neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function in guinea-pig lungs is inhibited by indomethacin.
Fryer AD, Okanlami OA.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Mar;147(3):559-64. PMID: 8442587
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8442587/
Effect of inflammatory cell mediators on M2 muscarinic receptors in the lungs.
|
Function of pulmonary M2 muscarinic receptors in antigen-challenged guinea pigs is restored by heparin and poly-L-glutamate.
Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2292-8. PMID: 1281829
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1281829/
Influenza virus A infection induces interleukin-8 gene expression in human airway epithelial cells.
Choi AM, Jacoby DB. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 14;309(3):327-9. PMID: 1516705
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1516705/
M2 muscarinic receptors inhibit isoproterenol-induced relaxation of canine airway smooth muscle.
Fernandes LB, Fryer AD, Hirshman CA.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):119-26. PMID: 1625190
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1625190/
Viral infection increases contractile but not secretory responses to substance P in ferret trachea.
Murray TC, Jacoby DB.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1992 Feb;72(2):608-11. PMID: 1373130
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1373130/
Virus-induced airway hyperresponsiveness--possible involvement of neural mechanisms.
Jacoby DB, Fryer AD.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Dec;144(6):1422-3. PMID: 1660232
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1660232/
Dysfunction of M2-muscarinic receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves after antigen challenge.
Fryer AD, Wills-Karp M.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1991 Dec;71(6):2255-61. PMID: 1778920
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1778920/
Infection of cultured human airway epithelial cells by influenza A virus.
|
Parainfluenza virus infection damages inhibitory M2 muscarinic receptors on pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig.
Fryer AD, Jacoby DB.Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):267-71. PMID: 1646059
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1646059/
Abnormalities in neural control of smooth muscle in virus-infected airways.
|
Parainfluenza virus type 1 reduces the affinity of agonists for muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig lung and heart.
Fryer AD, el-Fakahany EE, Jacoby DB.Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 31;181(1-2):51-8. PMID: 2167230
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2167230/
Identification of three muscarinic receptor subtypes in rat lung using binding studies with selective antagonists.
Fryer AD, el-Fakahany EE.Life Sci. 1990;47(7):611-8. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90572-9.PMID: 2402185
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2402185/
1984 - 1989
Different mechanisms of antagonism by methoctramine of two neuronal muscarinic receptor-mediated second messenger responses.
Lee NH, Fryer AD, Forray C, el-Fakahany EE.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):992-9. PMID: 2557423
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2557423/
Parainfluenza virus infection of cultured airway epithelial cells.
|
Virus induces airway hyperresponsiveness to tachykinins: role of neutral endopeptidase.
Dusser DJ, Jacoby DB, Djokic TD, Rubinstein I, Borson DB, Nadel JA.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1989 Oct;67(4):1504-11. PMID: 2477356
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2477356/
Identification of M1 muscarinic receptors in pulmonary sympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig by use of pirenzepine.
Maclagan J, Fryer AD, Faulkner D. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):499-505. PMID: 2758228
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2758228/
An endogenous factor induces heterogeneity of binding sites of selective muscarinic receptor antagonists in rat heart.
Fryer AD, el-Fakahany EE.Membr Biochem. 1989;8(3):127-32. PMID: 2641948
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2641948/
The effects of epithelial cell supernatant on contractions of isolated canine tracheal smooth muscle.
Barnett K, Jacoby DB, Nadel JA, Lazarus SC.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):780-3. PMID: 3202451
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3202451/
Influenza infection causes airway hyperresponsiveness by decreasing enkephalinase.
|
Effect of human eosinophil major basic protein on ion transport in dog tracheal epithelium.
Jacoby DB, Ueki IF, Widdicombe JH, Loegering DA, Gleich GJ, Nadel JA.Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jan;137(1):13-6. PMID: 3422142
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3422142/
Ipratropium bromide potentiates bronchoconstriction induced by vagal nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig.
Fryer AD, Maclagan J.Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 9;139(2):187-91. PMID: 2958300
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2958300/
Pancuronium and gallamine are antagonists for pre- and post-junctional muscarinic receptors in the guinea-pig lung.
Fryer AD, Maclagan J.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;335(4):367-71. PMID: 3600815
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3600815/
Postganglionic muscarinic inhibitory receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig.
Faulkner D, Fryer AD, Maclagan J.Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):181-7. PMID: 3708215
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3708215/
Ion transport across cat and ferret tracheal epithelia.
Corrales RJ, Coleman DL, Jacoby DB, Leikauf GD, Hahn HL, Nadel JA, Widdicombe JH.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986 Sep;61(3):1065-70. PMID: 3759745
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3759745/
Neuronal muscarinic receptors attenuate vagally-induced contraction of feline bronchial smooth muscle.
Blaber LC, Fryer AD, Maclagan J.Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):723-8. PMID: 2998526
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2998526/
The response of cat airways to histamine in vivo and in vitro.
Blaber LC, Fryer AD.Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):309-16. PMID: 2858235
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2858235/
Muscarinic inhibitory receptors in pulmonary parasympathetic nerves in the guinea-pig.
|